The Basics
What is trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is an infection caused by a protozoa called Trichomonas vaginalis. It is often called "Trich" (pronounced "Trick").
How common is trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is the most common curable STD in the United States. About 3.7 million people are currently infected with trichomoniasis in the US, but only 30% develop any symptoms. Females are more likely to get trichomoniasis than males, and older women are more likely to have it than younger women.
Where does trichomoniasis live?
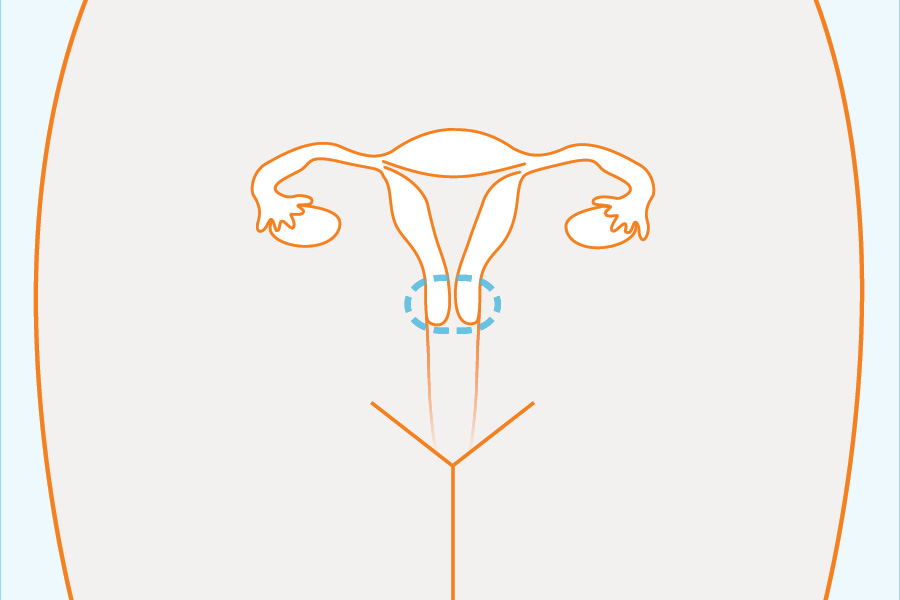
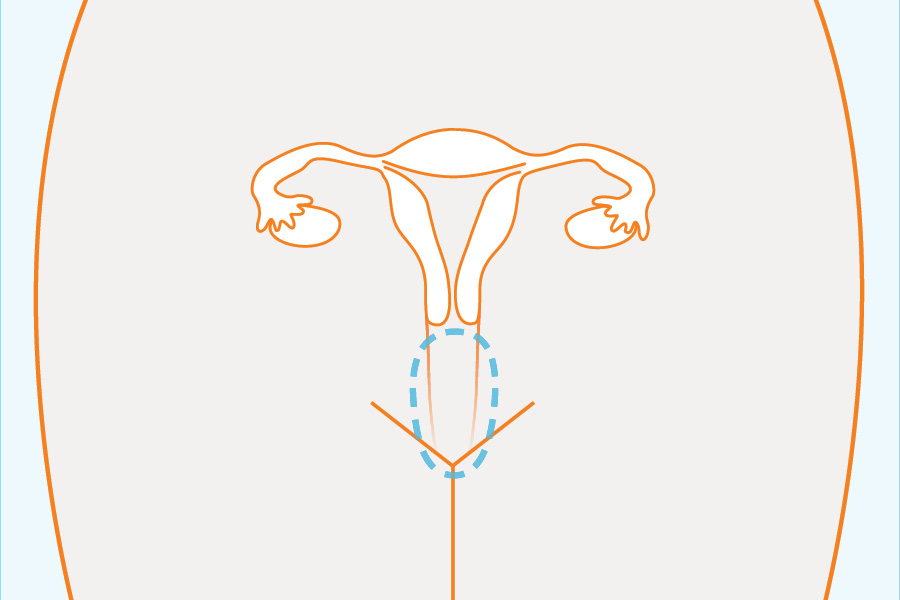
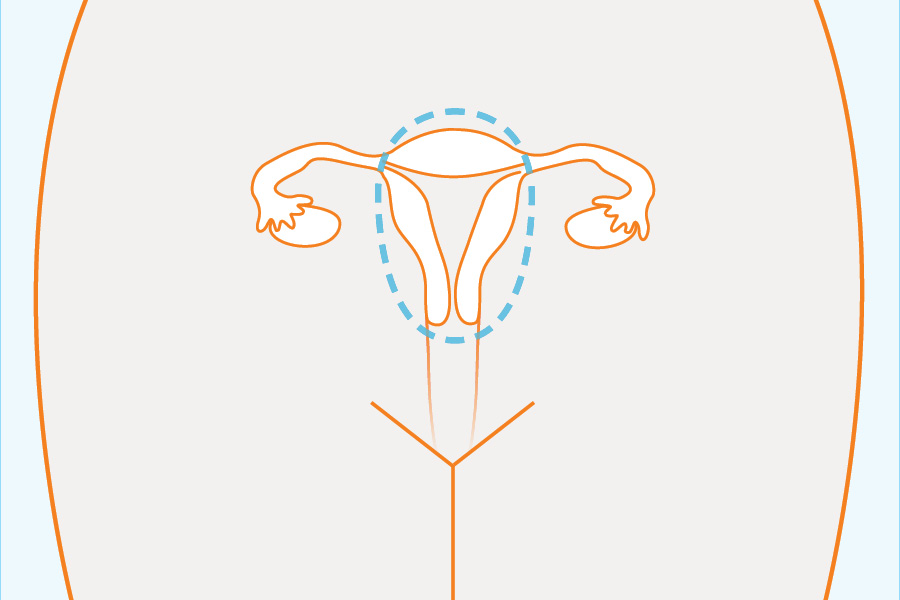
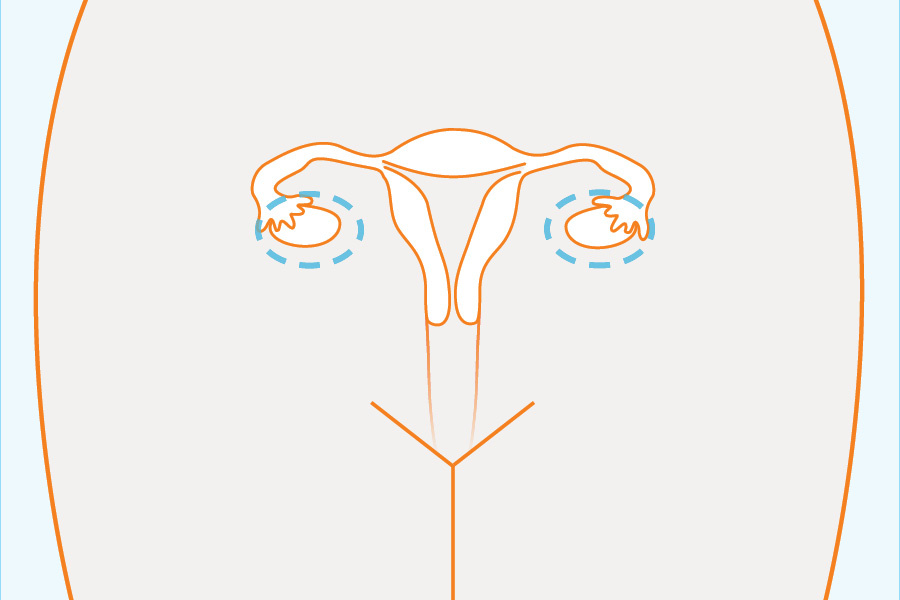
In females:
In males:
- Male reproductive system (inside the penis)
In males and females:
- Urethra (the hole and tube that pee comes out of)
It does not usually infect other body parts, like the hands, mouth, or anus. It can live outside the body for up to 45 minutes.
Symptoms and Disease
If I have trichomoniasis, will I develop symptoms?
Many people never have any symptoms. About 70% of people with trichomoniasis do not have symptoms. Although trichomoniasis affects both males and females, females are more likely to have symptoms than males.
What are the symptoms of trichomoniasis?
In females:
- A clear, green, yellowish, white, or grey discharge (fluid or material leaking) from the vagina
- Vaginal odor, often "fishy"
- Itching in or around the vagina
- Pain during sex
- Pain when urinating (peeing)
- Lower abdominal pain (rare cases)
In males:
- Itching or irritation inside the penis
- Discharge (fluid leaking when not ejaculating) from the penis
- Burning after urination or ejaculation
- Redness at end of penis
How quickly do the symptoms of trichomoniasis develop?
Females usually get symptoms 5-28 days after they have been infected. Males get symptoms 3-9 days after they have been infected. In some cases it can take a few months for symptoms to appear, and many people never show symptoms.
What can happen if I don't get treated for trichomoniasis?
For both males and females:
- Trich causes inflammation that makes it easier to get infected with the HIV virus or to pass the HIV virus on to a sex partner
For females:
- Pelvic infections
- Problems in pregnancy (like having babies born too early)
- Infertility (problems getting pregnant)
- Pregnant females can pass trichomoniasis to their babies
For males:
- Bladder infections
- Infected testicles
- Lower sperm count
Transmission
How is trichomoniasis spread?
It can be spread through:
- Vaginal sex (for both male and female partners)
- Vaginal-vaginal contact
Trichomoniasis can be spread from woman to woman, man to woman, or woman to man. It cannot be spread from man to man.
It can also be spread through the sharing of sex toys (used vaginally) between two women in a short time period. Sometimes, pregnant mothers who are infected may pass trichomoniasis to their female babies and cause babies to be born early or with low birth weight.
How can I prevent getting trichomoniasis?
- Abstain from (avoid) having vaginal, anal, and oral sex
- If you have vaginal or anal sex, use latex male condoms or female condoms
- If you have oral sex, use condoms or a latex or plastic barrier
- If you share insertive sex toys with your partners, wash the toys regularly and putting a male condom on the toy (which you change every time the toy is inserted into a new person).
- Do not share swimsuits or towels
It is important to know that you can get trichomoniasis even when your partner has no symptoms. For more tips, visit our Protect Page.
If I have trichomoniasis, how can I prevent giving it to someone else?
- Get treated, and don't have sex until 7 days after your treatment is done
- If you feel safe, tell your sex partners that you have the infection, so they can protect themselves and get tested.
- Once you are cured, use latex male condoms or female condoms when you have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
- Abstain from (avoid) having vaginal, anal, and oral sex
- If you share insertional sex toys with your partners, wash the toys regularly and putting a male condom on the toy (which you change every time the toy is inserted into a new person).
It is important to know that, if you are infected, you can give someone else trichomoniasis even when you don't have symptoms. For more tips, visit our Protect Page.
Can I still infect other people with trichomoniasis if I don't have symptoms?
Yes, even if you don't have symptoms, you can still spread trichomoniasis. Most people are not aware that they have the infection - especially men - and can infect others.
Am I more infectious with trichomoniasis at certain times?
You may be more likely to spread trichomoniasis if you also have another STD at the same time.
Tests, Results, & Treatment
How long do I have to wait to get tested for trichomoniasis?
You will only get tested for trichomoniasis if you have symptoms, so you have to wait until symptoms develop, usually 4-20 days after exposure.
How do you test for trichomoniasis?
For females, a clinician will take fluid from your vagina and look at it under a microscope or see if they can culture it (grow it in a lab dish). In order for the test to work it is important to not be on your period, to not douche, or use vaginal sprays or creams for 24 hours before the exam.
In males, testing is more difficult, but can be done by using urine, semen, or a swab of the inside of the penis and culturing it (growing it in a lab dish). It is harder to detect trichomoniasis in males than females.
How long do I have to wait for results from my trichomoniasis test?
Results can take 2 to 10 days, depending on where you got tested and where the lab is that your test will be sent. While you're waiting for your results, it's a good idea to use a condom when having sex or not have sex at all.
Where can I get tested for trichomoniasis?
A doctor or other healthcare professional may be able to test for trichomoniasis, or you can search for a clinic that can test you. See our Test Page for more information.
Is trichomoniasis curable?
Yes, trichomoniasis is curable.
What is the treatment for trichomoniasis?
Discuss treatment options with a doctor or other healthcare professional. Trichomoniasis can be cured with medications such as metronidazole or tinidazole. Be sure to take all the medication as directed, even if your symptoms go away. Do not drink alcohol while taking metronidazole, because the mix can be dangerous.
Any current sexual partners should also be treated. This will prevent you from getting re-infected with trichomoniasis. About 1 in 5 people get infected again within 3 months after treatment. Avoid having sex until after you and your partners have completed the treatment and you've stopped having symptoms, or you might not get rid of the infection.
Can I use medication I already have to treat trichomoniasis?
No. If your medication is old or the wrong type, it may not cure you.
Can I share my trichomoniasis medication with my partner?
No. You need to take all of your medication to get rid of the infection. A doctor or other healthcare professional might give you some medication specifically for your partner. If that happens, you can give that medication to your partners.
Do I need to do anything after I'm cured for trichomoniasis?
Avoid sexual contact until seven days after you and any partners have completed treatment. You should inform your partners and get tested again in three months.
Partner Notification
Should I notify my partner(s) if I have trichomoniasis?
Yes, if you feel safe doing so. Notify your past and current partners. In females, trichomoniasis can be easily tested for and cured. Males aren't routinely screened for it, so it might be harder to get tested for it.
Who should I notify if I have trichomoniasis?
There are no official rules for this. People will have different opinions on who you should notify. Here is what we suggest:
Past Partners: It depends on whether you are a male or female and whether or not you had symptoms.
If you had symptoms and are male:
You probably were infected sometime in the five weeks before your symptoms showed up. You were also infectious, and could have given a sexual partner trichomoniasis up until one week after you were treated. So we'd recommend notifying anyone you had vaginal, anal and/or oral sex with in the six weeks before you started having symptoms (to be safe) and anyone you had sex with since then. The picture below shows your "at-risk" period (the blue is the time when you might have had trich):
If you had symptoms and are female:
You probably were infected sometime in the two weeks before your symptoms showed up. You were also infectious, and could have given a sexual partner trichomoniasis up until one week after you were treated. So we'd recommend notifying anyone you had vaginal, anal and/or oral sex with in the three weeks before you developed symptoms (to be safe) and anyone you had sex with since then. The picture below shows your "at-risk" period (the blue is the time when you might have had trich):
If you didn't have symptoms and your trichomoniasis test before this one was negative:
You could have been infected or infected someone else one week before your last test (within the testing window). You were also infectious, and could have given a sexual partner trichomoniasis up until one week after you were treated. So we'd recommend notifying anyone you had vaginal, anal and/or oral sex with during that period of time. The picture below shows your "at-risk" period (the blue is the time when you might have had trich):
If you didn't have symptoms and your trichomoniasis test before this one was also positive:
You could have been infected or infected someone else from when you started treatment for your last infection. You were also infectious, and could have given a sexual partner trichomoniasis up until one week after you were treated. So we'd recommend notifying anyone you had vaginal, anal and/or oral sex with during that period of time. The picture below shows your "at-risk" period (the blue is the time when you might have had trich):
If you didn't have symptoms and you've never been tested for trichomoniasis before:
Anyone you have ever had vaginal sex with is at risk, or any woman you've had vaginal-vaginal contact with if you're a woman.
Current Partners: We recommend you tell anyone you are currently having sex with. You are infectious up until one week after you finish treatment, so consider telling anyone that you have sex with during that time.
Future Partners: Because trichomoniasis is curable, if you get treated and cured, you do not have to tell your future partners.
That's a lot of people to notify. Which of my partners are most at risk for trichomoniasis?
We recommend that you tell your current partners and anyone you've had sex with in the last two months. If you had symptoms, you may want to focus on notifying anyone you had sex with in the two months before you noticed your symptoms, and anyone you've had sex with since then until one week after completing treatment. Take the Partner Notification Quiz to learn more.